Organization

An organization (or organisation) is a group of people, operating within a defined structure, cooperating for some agreed-upon purpose.
Quotes
[edit]Pre-19th century
[edit]- Management of many is the same as management of few. It is a matter of organization.
- Sun Tzu (c. 6th century BC) The Art of War
- This great increase of the quantity of work which, in consequence of the division of labour, the same number of people are capable of performing, is owing to three different circumstances; first, to the increase of dexterity in every particular workman; secondly, to the saving of the time which is commonly lost in passing from one species of work to another; and lastly, to the invention of a great number of machines which facilitate and abridge labour, and enable one man to do the work of many.
- Adam Smith. The Wealth of Nations, (1776), Chapter I.
1800s
[edit]- It appears to me, that any explanation of the cheapness of manufactured articles, as consequent upon the division of labour, would be incomplete if the following principle were omitted to be stated.
- That the master manufacturer, by dividing the work to he executed into different processes, each requiring different degrees of skill or of force, can purchase exactly that precise quantity of both which is necessary for each process; whereas, if the whole work were executed by one workman, that person must possess sufficient skill to perform the most difficult, and sufficient strength to execute the most laborious, of the operations into which the art is divided.
- Charles Babbage, On the Economy of Machinery and Manufactures (1832) p. 175-6
- The establishment of "The Times" newspaper is an example, on a large scale, of a manufactory in which the division of labour, both mental and bodily, is admirably illustrated, and in which also the effect of domestic economy is well exemplified. It is scarcely imagined, by the thousands who read that paper in various quarters of the globe, what a scene of organized activity the factory presents during the whole night, or what a quantity of talent and mechanical skill is put in action for their amusement and information.
- Charles Babbage, On the Economy of Machinery and Manufactures (1832) p. 270; Ch. 28 "Proper circumstances for the application of machinery."
Man experiences a multitude of needs, on whose satisfaction his happiness depends, and whose non-satisfaction entails suffering. Alone and isolated, he could only provide in an incomplete, insufficient manner for these incessant needs. The instinct of sociability brings him together with similar persons, and drives him into communication with them. Therefore, impelled by the self-interest of the individuals thus brought together, a certain division of labor is established, necessarily followed by exchanges. In brief, we see an organization emerge, by means of which man can more completely satisfy his needs than he could living in isolation.
This natural organization is called society. The object of society is therefore the most complete satisfaction of man's needs. The division of labor and exchange are the means by which this is accomplished.
- Gustave de Molinari, J. Huston McCulloch (tr.), The Production of Security, Ludwig von Mises Institute, 1977/2009. orig. 1849.
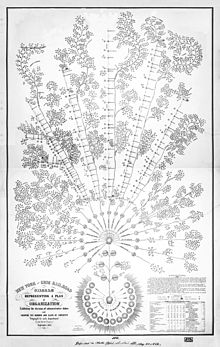
- The magnitude of the business of this road, its numerous and important connections, and. the large number of employés engaged in operating it, have led many, whose opinions are entitled to respect, to the conclusion, that a proper regard to details, which enter so largely into the elements of success in the management of all railroads, cannot possibly be attained by any plan that contemplates its organization as a whole ; and in proof of this position, the experience of shorter roads is referred to, the business operations of which have been conducted much more economically.
- Daniel McCallum (1855) "Report of the Superintendent of the New York and Erie Railroad to the Stockholders, for the Year Ending September 30" in: Annual Report. New York and Erie Railroad Company, 1856. p. 33: First paragraphs of the Report of the Superintendent.
- In my opinion a system of operations, to be efficient and successful, should be such as to give to the principal and responsible head of the running department a complete daily history of details in all their minutiae... A few general principles, however, may be regarded as settled and necessary in its formation, amongst which are:
- A proper division of responsibilities.
- Sufficient power conferred to enable the same to be fully carried out, that such responsibilities may be real in their character.
- The means of knowing whether such responsibilities are faithfully executed.
- Great promptness in the report of all derelictions of duty, that evils may be at once corrected.
- Such information, to be obtained through a system of daily reports and checks that will not embarrass principal officers, nor lessen their influence with their subordinates.
- The adoption of a system, as a whole, which will not only enable the General Superintendent to detect errors immediately, but will also point out the delinquent.
- Daniel McCallum (1855) "Report of the Superintendent of the New York and Erie Railroad to the Stockholders, for the Year Ending September 30" in: Annual Report. New York and Erie Railroad Company, 1856. p. 35-36: Partly cited in: George Leonard Vose. Handbook of Railroad Construction. J. Munroe, 1857. p. 415-16
- In the social production of their life, men enter into definite relations that are indispensable and independent of their will; these relations of production correspond to a definite stage of development of their material forces of production. The sum total of these relations of production constitutes the economic structure of society — the real foundation, on which rises a legal and political superstructure and to which correspond definite forms of social consciousness. The mode of production of material life determines the social, political and intellectual life process in general.
- Karl Marx, Preface to A Contribution to the Critique of Political Economy (1859).
- The directing motive, the end and aim of capitalist production, is to extract the greatest possible amount of surplus value, and consequently to exploit labor-power to the greatest possible extent.
- Karl Marx (1867), Das Kapital, "Buch I : Capital: A Critique of Political Economy," Ch. 13, pg. 363.
- Nowadays, the phenomenon (of division of labor) has developed so generally it is obvious to all. We need have no further illusions about the tendencies of modern industry; it advances steadily towards powerful machines, towards great concentrations of forces and capital, and consequently to the extreme division of labor. Occupations are infinitely separated and specialized, not only inside the factories, but each product is itself a specialty dependent upon others. Adam Smith and John Stuart Mill still hoped that agriculture, at least, would be an exception to the rule, and they saw it as the last resort of small-scale industry. Although one must be careful not to generalize unduly in such matters, nevertheless it is hard to deny today that the principal branches of the agricultural industry are steadily being drawn into the general movement. Finally, business itself is ingeniously following and reflecting in all its shadings the infinite diversity of industrial enterprises; and, while this evolution is realizing itself with unpremeditated spontaneity, the economists, examining its causes and appreciating its results, far from condemning or opposing it, uphold it as necessary. They see in it the supreme law of human societies and the condition of their progress.
- Émile Durkheim, The Division of Labor in Society (1893), p. 39
1900s
[edit]- The administrative function has many duties. It has to foresee and make preparations to meet the financial, commercial, and technical conditions under which the concern must be started and run. It deals with the organization, selection, and management of the staff. It is the means by which the various parts of the undertaking communicate with the outside world, etc. Although this list is incomplete, it gives us an idea of the importance of the administrative function. The sole fact that it is in charge of the staff makes it in most cases the predominant function, for we all know that, even if a firm has perfect machinery and manufacturing processes, it is doomed to failure if it is run by an inefficient staff.
- Henri Fayol, (1900) Henri Fayol addressed his colleagues in the mineral industry 23 June 1900
1910s
[edit]- In the railroad operation of this country an economy of $1,000,000 a day is possible.
- An attorney for the shippers (1910) cited in: ASME Sub-Committee on Administration, "The Present State of the Art of Industrial Management," ASME Transactions 34 (1912): p. 1131
- Statement made before the US Interstate Commerce Commission in a hearing on the matter of proposed advances in freight rates by carriers, November 21, 1910.

- Frederick Winslow Taylor (1911)
- In the past the man has been first; in the future the system must be first. This in no sense, however, implies that great men are not needed. On the contrary, the first object of any good system must be that of developing first-class men.
- Frederick Winslow Taylor (1911) Principles of Scientific Management, p. 2.
- The estimate that at least $1,000,000 a day could be saved by the pursuit of methods of scientific management was first made by Mr. Harrington Emerson. It is submitted that, with aggregate operating expenses by the railroads in 1908 of $1,669,938,717, of which $1,035,437,528 was for labor, this estimate appears moderate.
- United States. Interstate Commerce Commission, Martin Augustine Knapp (1911), Evidence Taken by the Interstate Commerce Commission in the Matter of Proposed Advances in Freight Rates by Carriers: August to December, 1910.
- According to Taylor, the principles of Efficiency are:
- (1) Science, not rule of thumb.
- (2) Harmony, not discord.
- (3) Cooperation, not competition.
- (4) Maximum output, not restricted output.
- (5) The development of each man to his greatest efficiency and prosperity.
- Herbert N. Casson. Ads and Sales: A Study of Advertising and Selling, from the Standpoint of new principles of scientific management. Published 1911, p. 8
- Comment: While later in the 20th century theory started to speak of management and organization, the scientific management movement spoke of management and efficiency. In a way the listed principles of efficiency are a listing of principles of organization.
- Modern industry is stated by some writers to have begun in 1738 when John Wyatt brought out a spinning machine. Others place the period as between 1750 and 1800, when the power loom and steam engine came into being. It was marked by the development of labor-saving machinery. It was brought about by the change from handicraft to manufacture.
- ASME Sub-Committee on Administration , "The Present State of the Art of Industrial Management : Majority Report of Sub-Committee on Administration," ASME Transactions 34 (1912): p. 1131
- Early British economists held that the application of the principle of division of labor was the basis of manufacture.... Charles Babbage, believed ... in [an] "Economy of Machinery and Manufacture." It appears, however, that another principle is the basic one in the rise of industry. It is the transference of skill. The transference of skill from the inventor or designer to the power-driven mechanism brought about the industrial revolution from handicraft to manufacture. It will be necessary to refer to this principle frequently throughout this report, in showing the meaning and position of management in industry.
- ASME Sub-Committee on Administration , "The Present State of the Art of Industrial Management : Majority Report of Sub-Committee on Administration," ASME Transactions 34 (1912): p. 1133
- The supreme principle [in Industrial Organization ] has been the belief that business efficiency and the welfare of the employees are but different sides of the same problem. Character is an economic asset ; and business efficiency depends not merely on the physical condition of employees, but on their general attitude and feeling towards the employer.
- Edward Cadbury. Experiments in industrial organization. (1912). Introduction, p. vii
- The test of any scheme of factory organization is the extent to which it creates and fosters the atmosphere and spirit of cooperation and good-will, without in any sense lessening the loyalty of the worker to his own class and its organizations.
- Edward Cadbury. Experiments in industrial organization. (1912). Introduction, p. vii
- The new industrial methods have greatly accelerated certain tendencies that had already manifested themselves in the old domestic factories and some of these deserve more than passing notice as they are affecting not only productive processes but our social organization as well. Perhaps the most important of these influences are those that tend toward
- (1) Aggregation or increase in size of industrial enterprises.
- (2) Specialization or the limiting of the field of activity, not only of enterprises but also of men.
- (3) Standardization or the reduction of all lines of product to a limited number of types and sizes.
- (4) Extreme division of labor, following aggregation, specialization, and standardization and requiring special consideration.
- These tendencies are all closely interlocked with each other, and with modern productive methods. It will be clearer, however, to discuss them separately before summing up their joint action.
- Dexter S. Kimball, Principles of industrial organization. New York : McGraw-Hill, 1913; 1919. p. 34
- Organization aims to unite individuals into a body which shall work together for a common end. Specifically, organization prepares for the transaction of business by electing and appointing officers and committees, delegating authorities and bringing into systematic connection and cooperation, each and every part of the industrial body. Right organization, in short, puts vitality into the entire factory, secures the efficient working-together of all employees, from the manager's office to the mechanic's bench, routes materials, sub-divides work, inspects output and delivers the right goods, fully processed, at the shipping room door on the correct delivery date.
- Clinton E. Woods (1914) "Charting authorities in the industrial body" in: Industrial organization. A.W. Shaw Company. p. 24
1920s
[edit]- The Methods of Industrial Management. — A committee of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers made an extensive canvass in the fall of 1912 to determine what were the new elements in modern management as well as what the committee designated as the regulative principles of industrial management. The committee confirmed Adam Smith's statement made in 1776 in his "Wealth of Nations," in which he held that the application of the principle of division of labor was the basis of manufacture. The committee also agreed with Charles Babbage, who in his work entitled "Economy of Machinery and Manufacture" written in 1832, added another principle, namely the transference of skill.
- Hugo Diemer (1921). Factory organization and administration, p. 10
- Tektology must clarify the modes of organization that are perceived to exist in nature and human activity; then it must generalize and systematize these modes; further it must explain them, that is, propose abstract schemes of their tendencies and laws; finally, based on these schemes, determine the direction of organizational methods and their role in the universal process. This general plan is similar to the plan of any natural science; but the objective of tektology is basically different. Tektology deals with organizational experiences not of this or that specialized field, but of all these fields together. In other words, tektology embraces the subject matter of all the other sciences and of all the human experience giving rise to these sciences, but only from the aspect of method, that is, it is interested only in the modes of organization of this subject matter.
- Alexander Bogdanov. Tektologia: Vseobshchaya Organizatsionnaya Nauka (Tektology. The Universal Organizational Science) (Moscow, Izdatelstvo Z. I. Grschebina, 1922. p. 82.
1930s
[edit]- Through all the years that I have been in business I have never yet found our business bad as a result of any outside force. It has always been due to some defect in our own company, and whenever we located and repaired that defect our business became good again - regardless of what anyone else might be doing. And it will always be found that this country has nationally bad business when business men are drifting, and that business is good when men take hold of their own affairs, put leadership into them, and push forward in spite of obstacles. Only disaster can result when the fundamental principles of business are disregarded and what looks like the easiest way is taken. These fundamentals, as I see them, are:
- (1) To make an ever increasingly large quantity of goods of the best possible quality, to make them in the best and most economical fashion, and to force them out onto the market.
- (2) To strive always for higher quality and lower prices as well as lower costs.
- (3) To raise wages gradually but continuously B and never to cut them.
- (4) To get the goods to the consumer in the most economical manner so that the benefits of low cost production may reach him.
- These fundamentals are all summed up in the single word 'service'... The service starts with discovering what people need and then supplying that need according to the principles that have just been given.
- Henry Ford in: Justus George Frederick (1930), A Philosophy of Production: A Symposium, p. 32; as cited in: Morgen Witzel (2003) Fifty Key Figures in Management. p. 196
- Organization is as old as human society itself.
- James D. Mooney Mooney and A.C. Reilley, Onward Industry!, New York: Harper and Bros, 1931. p. xiii.
- Organization is the arrangement of personnel for facilitating the accomplishment of some agreed purpose through the allocation of functions and responsibilities.
- John M. Gaus, "A theory of organization in public administration." The Frontiers of Public Administration (1936): 66.; Cited in Philip Selznick (1948, 25)
- An organization comes into being when (1) there are persons able to communicate with each other (2) who are willing to contribute action (3) to accomplish a common purpose. The elements of an organization are therefore (1) communication; (2) willingness to serve; and (3) common purpose. These elements are necessary and sufficient conditions initially, and they are found in all such organizations. The third element, purpose, is implicit in the definition. Willingness to serve, and communication, and the interdependence of the three elements in general, and their mutual dependence in specifie cooperative systems, are matters of experience and observation.
- Chester Barnard (1938) The Functions of the Executive p. 82
1940s
[edit]- The most important thing about organizations is that, though they are tools, each nevertheless has a life of its own.
- Philip Selznick (1949). TVA and the grass roots : a study in the sociology of formal organization, Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. p. 10
1950s
[edit]- Almost every organization... exhibits two faces — a smiling face which it turns toward its members and a frowning face which it turns to the world outside.
- Kenneth Boulding (1953) The Organizational Revolution: A Study in the Ethics of Economic Organization, Harper & Brothers. p. 10
- General Systems Theory... possibly the model of the world as a great organization can help to reinforce the sense of reverence for the living which we have almost lost.
- Ludwig von Bertalanffy (1955) "General System Theory". In: Main Currents in Modern Thought 11: pp.75-83.
- Today our main problem is that of organized complexity. Concepts like those of organization, wholeness, directiveness, teleology, control, self-regulation, differentiation and the like are alien to conventional physics. However, they pop up everywhere in the biological, behavioural and social sciences, and are, in fact, indispensable for dealing with living organisms or social groups. Thus, a basic problem posed to modern science is a general theory of organization.
- Ludwig von Bertalanffy (1956) "General System Theory". In: General Systems, Yearbook of the Society for General Systems Research, vol. 1, 1956.
- As a formal analytical point of reference, primacy of orientation to the attainment of a specific goal is used as the defining characteristic of an organization which distinguishes it from other types of social systems.
- Talcott Parsons (1956: 64); Partly cited in: Chiara Demartini (2013). Performance Management Systems: Design, Diagnosis and Use. p. 17
- It isn't the incompetent who destroy an organization. The incompetent never get into a position to destroy it. It is those who have achieved something and want to rest upon their achievements who are forever clogging things up.
- Charles E. Sorensen (1956) My Forty Years with Ford, New York, New York, USA: Norton. p. 51
- Management has a design and operation function, as does engineering. The design is usually done under the heading of organization. It should be noted first that the performance of a group of people is a strong function of the capabilities of the individuals and a rather weak function of the way they are organized. That is, good people do a fairly good job under almost any organization and a somewhat better one when the organization is good. Poor talent does a poor job with a bad organization, but it is still a poor job no matter what the organization. Repeated reorganizations are noted in groups of individuals poorly suited to their function, though no amount of good organization will give good performance. The best architectural design fails with poor bricks and mortar. But the payoff from good organization with good people is worthwhile.
- Robert E. Machol, Harry H. Goode (1957) System Engineering: An Introduction to the Design of Large-scale Systems. McGraw-Hill. p. 514
- An organization is a group of living human beings. The formal or official design for living never completely accounts for what the participants do. It is always supplemented by what is called the “informal structure,” which arises as the individual brings into play his own personality, his special problems and interests. Formal relations co-ordinate roles or specialized activities, not persons.
- Philip Selznick, Leadership in Administration: A Sociological Interpretation, 1957, 2011. p. 8
- Organization is a mechanism or structure that enables living things to work effectively together.
- Louis A. Allen. Management and organization, McGraw-Hill, 1958.
1960s
[edit]- Formal theories of organization have been taught in management courses for many years, and there is an extensive literature on the subject. The textbook principles of organization — hierarchical structure, authority, unity of command, task specialization, division of staff and line, span of control, equality of responsibility and authority, etc. — comprise a logically persuasive set of assumptions which have had a profound influence upon managerial behavior.
- Douglas McGregor (1960), The Human Side of Enterprise; p. 15. Annotated Edition, 2006, p. 21.
- Classical organization theory suffers from "ethnocentrism": It ignores the significance of the political, social, and economic milieu in shaping organizations and influencing managerial practice.
- Douglas McGregor (1960), The Human Side of Enterprise; p. 16. Annotated Edition, 2006, p. 23.
- The scientific study of leadership in complex organizations, as an area of enquiry in its own right, is relatively new; hardly more than a decade old. As in any new "science" there is yet no comprehensive framework within which to operate. Unlike medical men after Harvey's great discovery on the circular system of the human body, we have no unifying concepts around which to make further refinements and discoveries.
- Ernest Dale modestly recognizes this fact. In The Great Organizers he takes the position that before we proceed too far in theory it is first necessary to known the history and the terrain of the subject. His vehicle is the case history in depth; his method is the comparative historical approach, not deduction based on a comprehensive model.
- Robert H. Guest. "Reviewed Work: The Great Organizers by Ernest Dale," Technology and Culture, Vol. 3, No. 3 (Summer, 1962), pp. 349-351
- The basic problem of social organization is how to co-ordinate the economic activities of large numbers of people.
- Milton Friedman Capitalism and Freedom (1962) Ch. 1 The Relation Between Economic Freedom and Political Freedom
- I firmly believe that any organization, in order to survive and achieve success, must have a sound set of beliefs on which it premises all its policies and actions.
Next I believe that the most important single factor in corporate success is faithful adherence to those beliefs.
And, finally I believe if an organization is to meet the challenge of a changing world, it must be prepared to change everything about itself except those beliefs as it moves through corporate life.
Basic philosophy, spirit and drive of an organization have far more to do with its relative achievements than do technological or economic resources, organizational structure, innovation and timing...- Thomas Watson, Jr. (1962) as cited in: Heather Clark, John Chandler, Jim Barry (1994) Organisation and Identities: : Text and Readings in Organizational Behaviour. p. 355
- Social organizations are flagrantly open systems in that the input of energies and the conversion of output into further energy input consists of transactions between the organization and its environment.
- Daniel Katz & Robert L. Kahn (1966), The Social Psychology of Organizations. p. 16-17
- The inevitable counterpart of specialization is organization. This is what brings the work of specialists to a coherent result. If there are many specialists, this coordination will be a major task. So complex, indeed, will be the job of organizing specialists that there will be specialists on organization and organizations of specialists on organization. More perhaps than machinery, massive and complex business organizations are the tangible manifestation of advanced technology.
- John Kenneth Galbraith, The New Industrial State (1967), p. 16
- The greatest mistake of the movement has been trying to organize a sleeping people around specific goals. You have to wake the people up first, then you'll get action.
- Malcolm X, in Village Voice interview, February 1965, in By Any Means Necessary, p. 21
1970s
[edit]
- People do not exist just for organizations. They track all kinds of mud from the rest of their lives into the organization, and they have all kinds of interests that are independent of the organization.
- Charles Perrow (1972, Complex organizations: a critical essay, Random House, p. 4
- During the last fifty years, society in every developed country has become a society of institutions. Every major social task, whether economic performance or health care, education or the protection of the environment, the pursuit of new knowledge or defense, is today being entrusted to big organizations, designed for perpetuity and managed by their own managements.
- Peter Drucker, Management: Tasks, Responsibilities, Practices, (1973), p. 3.
- No organization chart is likely ever to be displayed in a major art museum. What matters is not the chart but the organization. A chart is nothing but an oversimplification which enables people to make sure that they talk about the same things in discussing organization. One never makes.
- Peter Drucker (1973) Management. p. 547-8.
- The purpose of an organization is to enable common men to do uncommon things.
- Peter Drucker MANAGEMENT: Tasks, Responsibilities, Practices (1973) Chapter 36, pg. 455
- There is no one best way to organize... Any way of organizing is not equally effective.
- Jay R. Galbraith, Designing complex organizations, 1973. p. 2: The two underlying assumptions of contingency theory.
- All organisations have to make provision for continuing activities directed towards the achievement of given aims. Regularities in activities such as task allocation, supervision, and co-ordination are developed. Such regularities constitute the organisation’s structure, and the fact that these activities can be arranged in various ways means that organisations can have differing structures.
- Pugh, D. and Hickson, D. (1973). The comparative study of organizations. In Salaman, G. and Thompson, K., editors, People and Organizations, Longmans, London. pp 50–66. Cited in: Andreas Schaad. (2003) A Framework for Organisational Control Principles. p. 24
- Organization design is conceived to be a decision process to bring about a coherence between the goals or purposes for which the organization exists, the patterns of division of labor and interunit coordination and the people who will do the work.
- Jay R. Galbraith (1977). Organization design. p. 5
- Organizations are goal-directed, boundary-maintaining, activity systems.
- Howard E. Aldrich (1979). Organizations and Environments, p. 4

- Mintzberg (1979)
- Given the five parts of the organization - operating core, strategic apex, middle line, technostructure, and support staff - we may now ask how they all function together. In fact, we cannot describe the one way they function together, for research suggests that the linkages are varied and complex. The parts of the organization are joined together by different flows - of authority, of work material, of information, and of decision processes (themselves informational).
- Henry Mintzberg (1979) The structuring of organizations: A synthesis of the research p. 35
- If an organization is to learn anything, then the distribution of its memory, the accuracy of that memory, and the conditions under which that memory is treated as a constraint become crucial characteristics of organizing.
- Karl E. Weick (1979; 206), cited in: James P. Walsh and Gerardo Rivera Ungson. "Organizational memory." Academy of management review 16.1 (1991): 57-91.
1980s
[edit]- Any approach to the study of organizations is built on specific assumptions about the nature of organizations and how they are designed and function.
- R.L. Daft, Karl E. Weick. "Toward a model of organizations as interpretation systems," Academy of management review, 1984.
- Institutional theories of organization provide a rich, complex view of organizations. In these theories, organizations are influenced by normative pressures, sometimes arising from external sources such as the state, other times arising from within the organization itself. Under some conditions, these pressures lead the organization to be guided by legitimated elements, from standard operating procedures to professional certification and state requirement, which often have the effect of directing attention away from task performance... Institutional theories of organization have spread rapidly, a testimony to the power of the imaginative ideas developed in theoretical and empirical work.
- Lynne G. Zucker (1987). "Institutional Theories of Organization," In: Annual Review of Sociology Vol. 13: 443-464
- We create organizations to serve us, but somehow they also force us to serve them. Sometimes it feels as if our institutions have run out of control, like the machinery of Charlie Chaplin's film Modem Times. Why we should become slaves to our servants... A society of organizations is one in which organizations enter our lives as influential forces in a great many ways — in how we work, what we eat, how we get educated and cured of our illnesses, how we get entertained, and how our ideas are shaped. The ways in which we try to control our organization and our organization in return try to control us become major issues in the lives of all of us.
- Henry Mintzberg (1989) Mintzberg on management: inside our strange world of organizations. p. 301. As cited in: R. van den Nieuwenhof (2003) 2 strategie: omgaan met de omgeving. p. 36
1990s
[edit]- The things we fear most in organizations - fluctuations, disturbances, imbalances - need not be signs of an impending disorder that will destroy us. Instead, fluctuations are the primary source of creativity.
- Margaret Wheatley (1992) Leadership and the New Science. p. 19-20 as cited in: Michael C. Jackson (2000) Systems Approaches to Management. p. 77
- Organizations are systems of coordinated action among individuals and groups whose preferences, information, interests, or knowledge differ. Organization theories describe the delicate conversion of conflict into cooperation, the mobilization of resources, and the coordination of effort that facilitate the joint survival of an organization and its members.
- James G. March, and Herbert A. Simon. "Organizations revisited." Industrial and Corporate Change 2.1 (1993): 299-316.
- We are organizational creatures. We are born not only into a society and culture but usually into a specific, complex organization: a family. Our marriages are organizations. We study in schools that are organizations; we earn a living in businesses that are organizations; at some time or another we will likely worship in an organization; and when we die there will be organizations to usher us out of this world.
- Peck, M. Scott (1993). "Something is Seriously Wrong". A World Waiting to Be Born. pp. 5.
- We don't know what organization is. ...We do know that complex adaptive systems have to be nonlinear and capable of storing information. ...We know a little bit about what distinguishes an adaptive complex system from a nonadaptive system, such as turbulent fluid flow.
- J. Doyne Farmer, The Third Culture: Beyond the Scientific Revolution (1995)
- By organization Maturana refers to the relations between components that give a system its identity, that make it a member of a particular type. Thus, if the organization of a system changes, so does its identity. By structure Maturana means the actual components and relations between components that constitute a particular example of a type of system. The organization is realized through the structure, but it is the structure that can interact and change. So long as the structural changes maintain the organization, the system’s identity remains.
- John Mingers, Self-Producing Systems: Implications and Applications of Autopoiesis. Contemporary Systems Thinking. New York: Plenum P, 1995
2000s
[edit]- The Internet is the technological basis for the organizational form of the Information Age: the network."
- Manuel Castells, The Internet Galaxy - Reflections on the Internet, Business, and Society (2001). p. 1; Opening, The Network is the Message.
- Cultures are not made from free-floating values. They are rooted in institutions and organizations.
- Manuel Castells, The Internet Galaxy - Reflections on the Internet, Business, and Society (2001). p. 48
- Self-organization [is] the appearance of structure or pattern without an external agent imposing it.
- Francis Heylighen (2001) "The science of self-organization and adaptivity" in: The Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems 5 (3), p. 253-280
- Until I came to IBM, I probably would have told you that culture was just one among several important elements in any organization's makeup and success — along with vision, strategy, marketing, financials, and the like... I came to see, in my time at IBM, that culture isn't just one aspect of the game, it is the game. In the end, an organization is nothing more than the collective capacity of its people to create value.
- Louis V. Gerstner, Jr. Who Says Elephants Can’t Dance? (2002)
- In organizations, real power and energy is generated through relationships. The patterns of relationships and the capacities to form them are more important than tasks, functions, roles, and positions.
- Margaret Wheatley, as quoted in 100 Ways to Motivate Yourself (2004) by Steve Chandler, p. 123
- Any social organization does well enough if it isn't rigid. The framework doesn't matter as long as there is enough looseness to permit that one man in a multitude to display his genius. Most so-called social scientists seem to think that organization is everything. It is almost nothing — except when it is a straitjacket. It is the incidence of heroes that counts, not the pattern of zeros.
- Robert A. Heinlein (2007), Glory Road, p. 277
- From a legal point of view, an organisation is a legal person. It is legitimised, under the laws of the land, by a legally recognised and binding constitution specifying purpose, procedures to be followed, hierarchical offices to be taken up, authority to be granted, and membership criteria and categories.
- Ralph Douglas Stacey (2007), Strategic Management and Organisational Dynamics. p. 316.
- We use the word "organization" to mean both the state of being organized and the groups that do the organizing... We use one word for both because, at a certain scale, we haven't been able to get organization without organizations; the former seems to imply the latter.
- Clay Shirky, Here Comes Everybody: The Power of Organizing Without Organizations, 2008. p. 29
2010s
[edit]- Organizations are (1) social entities that (2) are goal-directed, (3) are designed as deliberately structured and coordinated activity systems, and (4) are linked to the external environment.
- Richard L. Daft, Jonathan Murphy, Hugh Willmott (2010) Organization Theory and Design, p. 10; Cited in: Jan A. P. Hoogervorst (2009), Enterprise Governance and Enterprise Engineering, p. 80.
- The essence of an organisation is not the bricks, or the people, but the means in which these are combined.
- Paul Griseri (2013). An Introduction to the Philosophy of Management. p. 20
- A corporation is a group of people, and if you want to come together for profit or nonprofit, that's your business—whatever you want to do.
- Krist Novoselic, interviewed by Nick Gillespie, "Nirvana's Krist Novoselic on Punk, Politics, & Why He Dumped the Dems", ReasonTV (19 June 2014), 17:10–17:20.
See also
[edit]- Companies
- Learning organization
- Corporations
- Organization chart
- Organizational culture
- Organizational design
- Organizational structure
- Organizational theory
- Principles of organization
- Civil society


